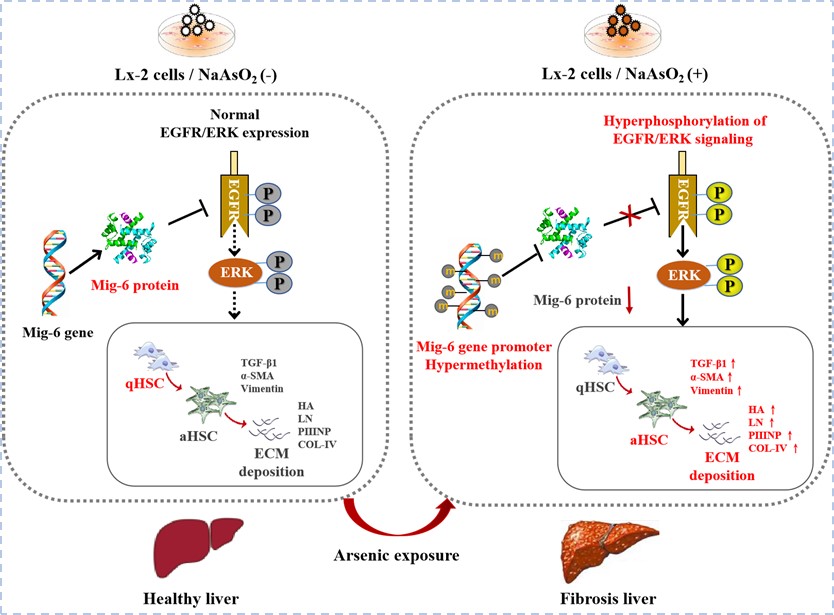
2022年10月,我室王大朋副教授、硕士生阮文丽、博士生范丽丽为共同第一作者,王大朋副教授、张爱华教授为共同通讯作者在著名国际期刊《有害材料》(Journal of Hazardous Materials;中科院一区Top期刊,IF:14.224)发表题为“Hypermethylation of Mig-6 gene promoter region inactivates its function, leading to EGFR/ERK signaling hyperphosphorylation, and is involved in arsenite-induced hepatic stellate cells activation and extracellular matrix deposition”的研究论文。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金项目和贵州省优秀青年科学基金的支持。

砷是一种广泛存在于自然界的环境污染物,既往研究发现砷暴露可引起肝纤维化损伤,但其确切分子机制尚不清楚。该研究从信号通路调控和表观遗传修饰两方面来探讨Mig-6/EGFR信号通路在砷诱导的人肝星状细胞(HSCs)活化及细胞外基质(ECM)沉积中的作用及机制。研究结果显示,亚砷酸钠暴露可显著诱导HSCs活化和ECM沉积,同时引起EGFR/ERK信号通路磷酸化活化,EGFR负反馈调控基因Mig-6的失活参与上述过程。进一步采用亚硫酸修饰后PCR技术(BSP)及DNA甲基转移酶抑制剂5-Aza-dC干预证实了砷致Mig-6基因启动子区DNA高甲基化是导致Mig-6基因失活的主要原因,5-Aza-dC干预后可显著抑制砷暴露所致HSCs活化及ECM沉积。上述发现对深入了解砷致肝纤维化损伤分子机制及针对性防治具有重要科学意义。
时间:2022年10月
刊物:Journal of Hazardous Materials
标题:Hypermethylation of Mig-6 gene promoter region inactivates its function, leading to EGFR/ERK signaling hyperphosphorylation, and is involved in arsenite-induced hepatic stellate cells activation and extracellular matrix deposition